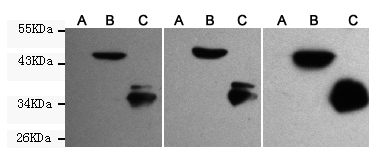
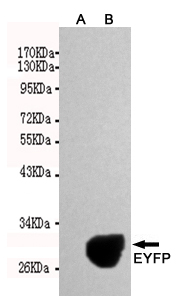
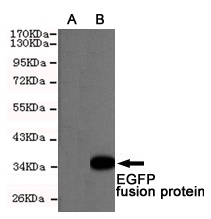
The green fluorescent protein (GFP) is a protein isolated from the jellyfish Aequorea victoria composed of 238 amino acid residues that exhibits bright green fluorescence. GFP has become a very useful tool as a fusion protein that reports gene expression, traces cell lineages and defines subcellular protein localizations. Due to the potential for widespread usage and the evolving needs of researchers, many different mutants of GFP have been engineered. For example, EGFP contains the double-amino-acid substitution of Phe-64 to Leu and Ser-65 to Thr which result in brighter green fluorescence. EYFP contains the four amino acid substitutions of Ser-65 to Gly; Val-68 to Leu; Ser-72 to Ala; and Thr-203 to Tyr. EYFP emits yellow fluorescence excited by green light.