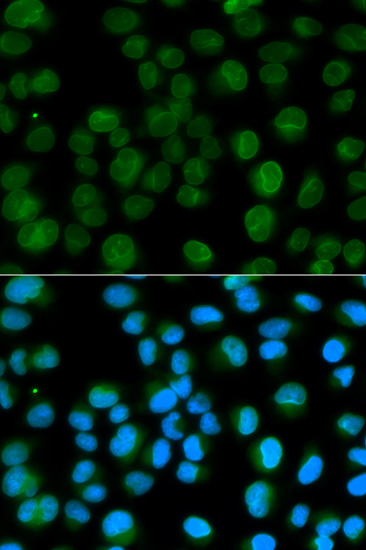
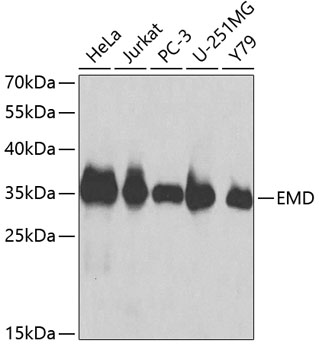
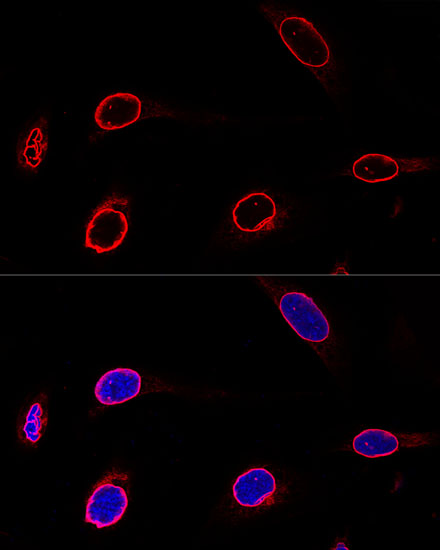
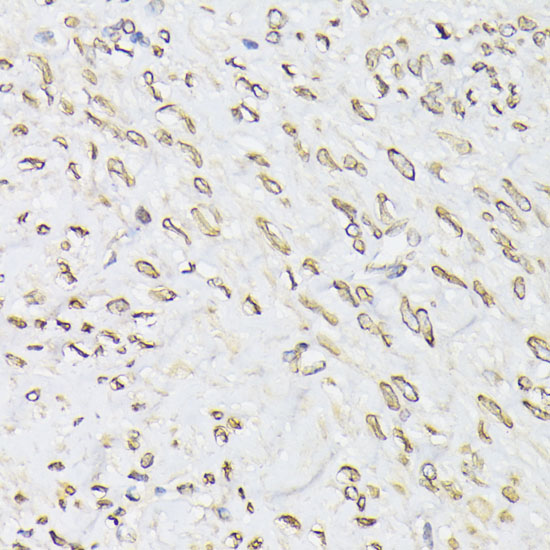
Emerin is a broadly expressed integral protein of the nuclear inner membrane (1). It contains a LEM domain and binds to several nuclear proteins, such as BAF (barrier-to-autointegration factor) and A- and B-type lamins, which are important in nuclear functions (2-5). Emerin may regulate gene expression through binding to other transcriptional regulators (6,7). Emerin binds to β-catenin and inhibits its nuclear accumulation (8). Recent studies demonstrate that Emerin is required for HIV-1 infectivity (9). Mutations in Emerin are a major cause of Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (EDMD), a disorder characterized by progressive skeletal muscle weakening (10).