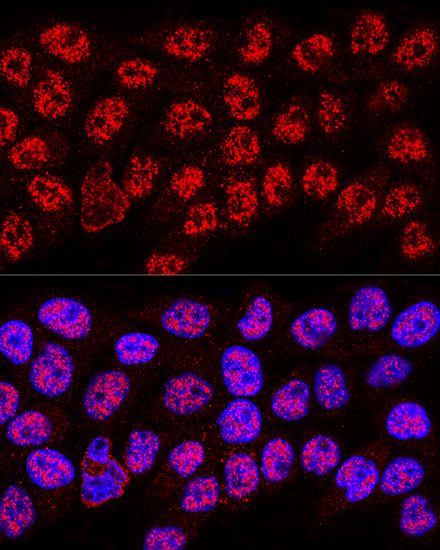
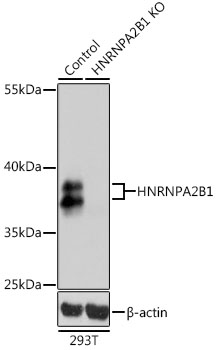
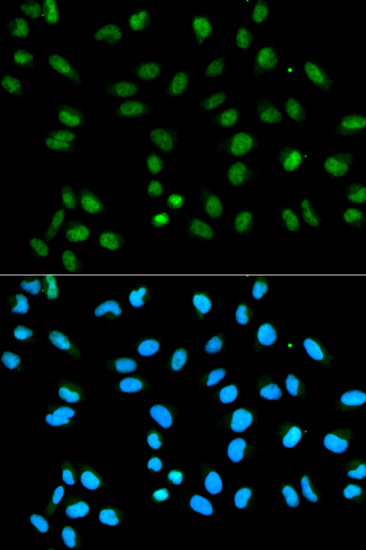
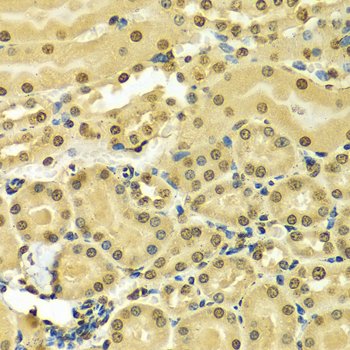
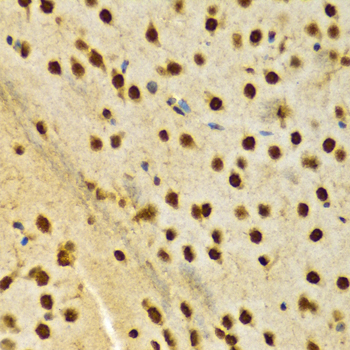
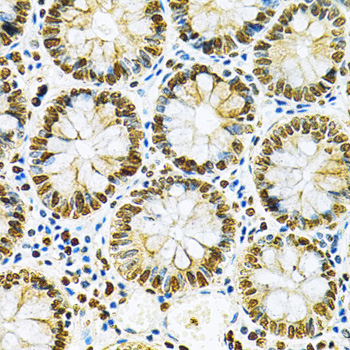
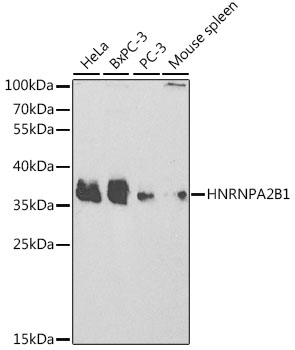
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2/B1 (hnRNP A2/B1) is a member of the hnRNP A/B family of related RNA binding proteins that bind pre-mRNA and are involved in the processing, metabolism and transport of nuclear pre-mRNA transcripts (1). Alternative splicing produces transcripts that encode two homologous hnRNP proteins, hnRNPA2 and hnRNPB1, from a single gene sequence (2). Studies demonstrate hnRNP A2/B1 splicing repression across multiple targets (3,4) and that both proteins can bind and protect telomere repeat sequences from DNase digestion (5,6). Altered expression of hnRNP B1 is seen in several forms of cancer, including squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, and various forms of lung cancer (7). Over expression of hnRNP B1 may be associated with inhibition of DNA-PK activity and impaired DNA repair during early stages of cancer development (8). Autoantigens to hnRNP A2/B1 (termed RA33) are associated with rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythromatosus and mixed connective tissue disease (9-11).