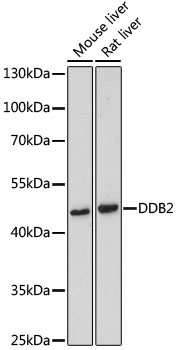
Damaged DNA-Binding Protein (DDB) consists of a 127 kDa subunit (DDB-1) and a 48 kDa subunit (DDB-2) that contribute to the formation of the UV-damaged DNA-binding protein complex (UV-DDB) (1-3). In conjunction with CUL4A and ROC-1, the UV-DDB complex forms an E3 ubiquitin ligase that recognizes a broad spectrum of DNA lesions such as cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers, 6-4 photoproducts, apurinic sites and short mismatches. The complex polyubiquitinates components of the nucleotide excision repair pathway (4-6). Loss of DDB activity has been identified in a subset of xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group E (XP-E) patients and has been linked to the deficient repair of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers in cells derived from these patients (7-10).