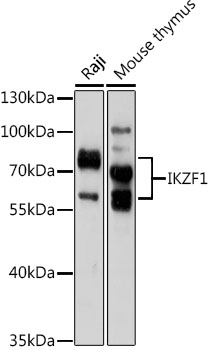
Ikaros family proteins, characterized by the presence of an N-terminal zinc finger DNA-binding domain and a C-terminal dimerization domain, belong to the Kruppel transcription factor superfamily. The Ikaros family includes Ikaros, Aiolos, Helios, and possibly EOS and Pegasus (1). They can form homodimers and heterodimers with other members of the Ikaros family. Due to differential splicing, multiple isoforms can be generated and some behave in a dominant negative manner upon dimerization (2).Ikaros, also known as Ikaros family zinc finger protein 1 (IKZF1) and Lymphoid transcription factor 1 (LYF-1), is expressed abundantly in blood cells. Genetic studies in mice demonstrate that Ikaros is important for the normal development of B, T, natural killer, and dendritic cells, and that it functions as a tumor suppressor (3,4). Research studies have shown that imbalanced expression of different Ikaros isoforms, as well as deletions of Ikaros are associated with hematologic malignancies in humans (5-7).