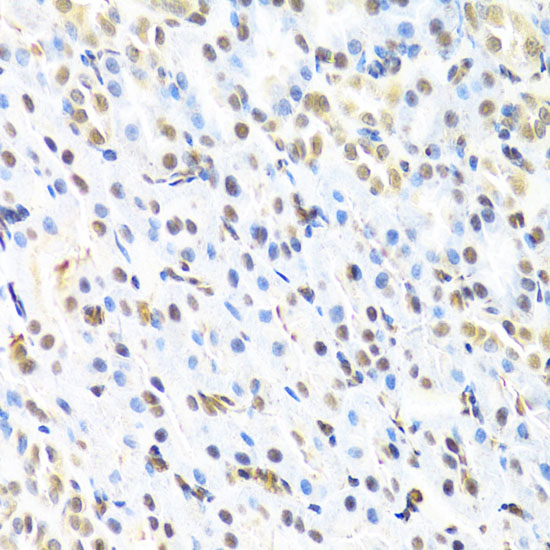
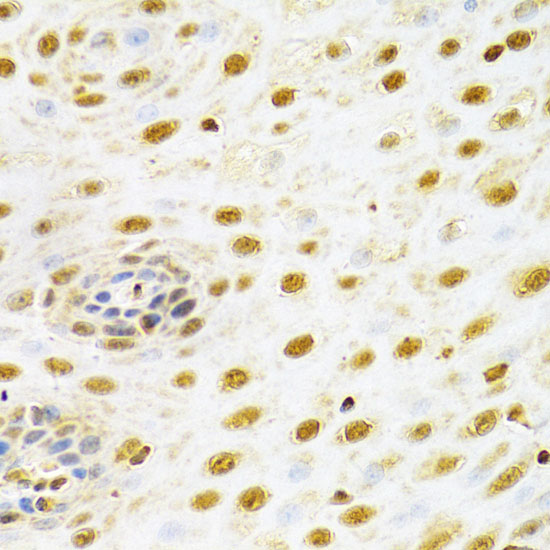
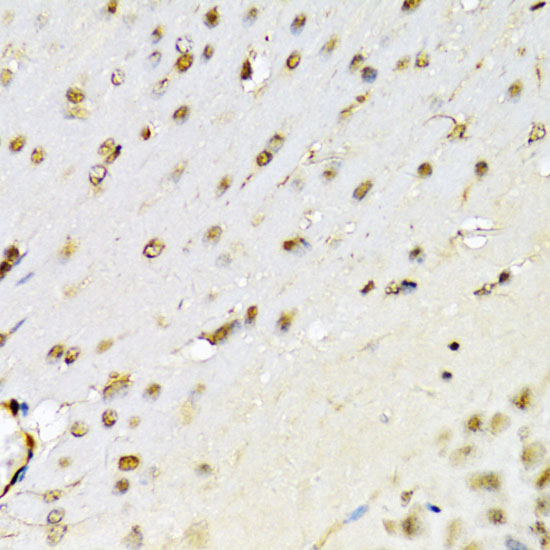
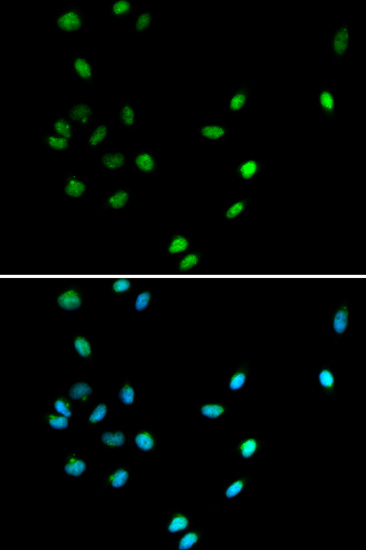
AML1 (also known as Runx1, CBFA2, and PEBP2αB) is a member of the core binding factor (CBF) family of transcription factors (1,2). It is required for normal development of all hematopoietic lineages (3-5). AML1 forms a heterodimeric DNA binding complex with its partner protein CBFβ and regulates the expression of cellular genes by binding to promoter and enhancer elements. AML1 is commonly translocated in hematopoietic cancers: chromosomal translocations include t(8;21) AML1-ETO, t(12;21) TEL-AML, and t(8;21) AML-M2 (6). Phosphorylation of AML1 on several potential serine and threonine sites, including Ser249, is thought to occur in an Erk-dependent manner (7,8).