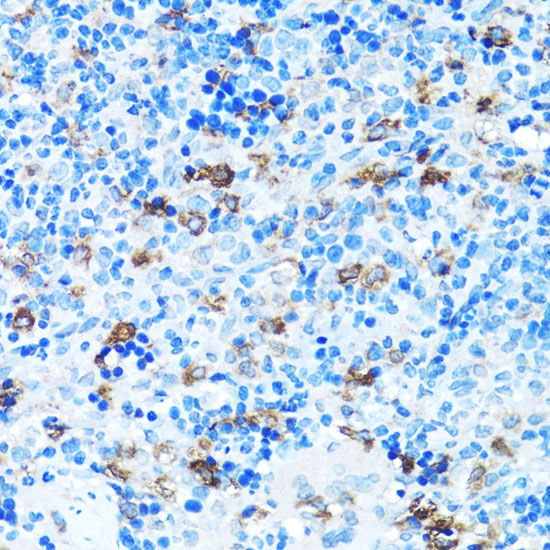
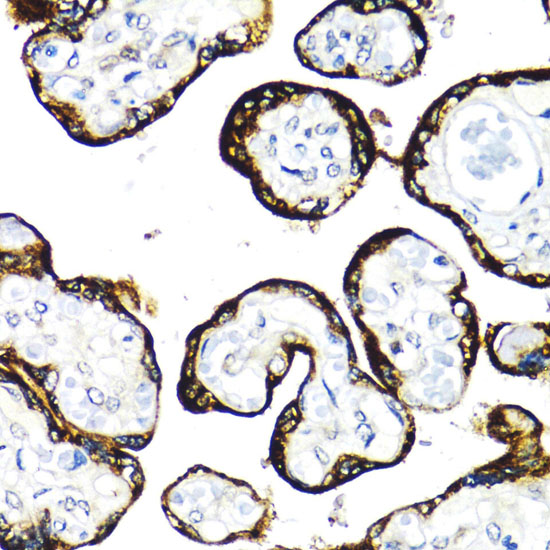
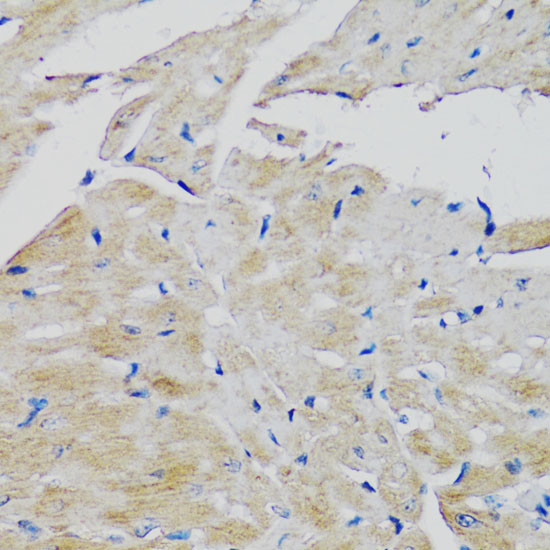
Fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) produce mitogenic and angiogenic effects in target cells by signaling through cell surface receptor tyrosine kinases. There are four members of the FGF receptor family: FGFR1 (flg), FGFR2 (bek, KGFR), FGFR3, and FGFR4. Each receptor contains an extracellular ligand binding domain, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic kinase domain (1). Following ligand binding and dimerization, the receptors are phosphorylated at specific tyrosine residues (2). Seven tyrosine residues in the cytoplasmic tail of FGFR1 can be phosphorylated: Tyr463, 583, 585, 653, 654, 730, and 766. Tyr653 and Tyr654 are important for catalytic activity of activated FGFR and are essential for signaling (3). The other phosphorylated tyrosine residues may provide docking sites for downstream signaling components such as Crk and PLCγ (4,5).