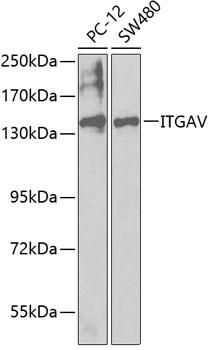
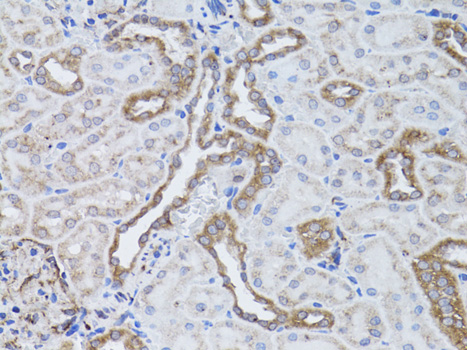
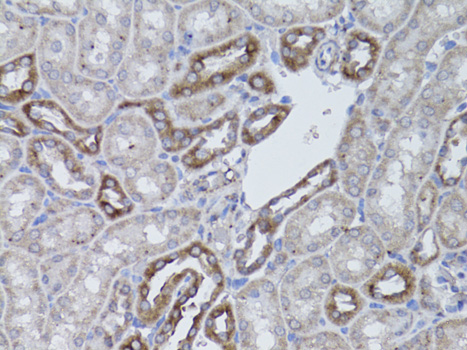
Integrins are α/β heterodimeric cell surface receptors that play a pivotal role in cell adhesion and migration, as well as in growth and survival (1,2). The integrin family contains at least 18 α and 8 β subunits that form 24 known integrins with distinct tissue distribution and overlaping ligand specificities (3). Integrins not only transmit signals to cells in response to the extracellular environment (outside-in signaling), but also sense intracellular cues to alter their interaction with extracellular environment (inside-out signaling) (1,2).Several αV subfamily members, including αVβ3, αVβ5, αVβ1, are highly expressed in active endothelial cells and cancer cells (3-6) where they play a critical role in angiogenesis and tumor metastasis (7-9). Therefore, interest has focused on αV integrin as a key therapeutic target in the treatment of cancer (10-12).