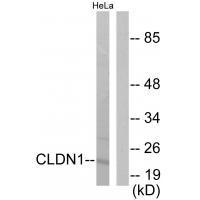
Claudins function as major constituents of the tight junction complexes that regulate the permeability of epithelia. While some claudin family members play essential roles in the formation of impermeable barriers, others mediate the permeability to ions and small molecules. Often, several claudin family members are coexpressed and interact with each other, and this determines the overall permeability. CLDN1 is required to prevent the paracellular diffusion of small molecules through tight junctions in the epidermis and is required for the normal barrier function of the skin. Required for normal water homeostasis and to prevent excessive water loss through the skin, probably via an indirect effect on the expression levels of other proteins, since CLDN1 itself seems to be dispensable for water barrier formation in keratinocyte tight junctions (). CLDN1 acts as a coreceptor for HCV entry into hepatic cells.
Julie Dufresne and Daniel G. Cyr, Biol Reprod, May 2007; 76: 825 - 832.
Evemie Dub¨¦, Biol Reprod, Apr 2007; 10.1095/biolreprod.106.059246.
Michele A. Battle, PNAS, May 2006; 103: 8419 - 8424.
Edmund C. Chang, Endocrinology, Oct 2006; 147: 4831 - 4842.