Product Detail
Product NameATP1A1 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Host SpeciesRabbit
ClonalityPolyclonal
IsotypeIgG
PurificationAffinity purification
ApplicationsWB,IHC
Species ReactivityHuman,Mouse,Rat
Immunogen DescA synthetic peptide of human Na+/K+-ATPase (NP_000692.2).
ConjugateUnconjugated
Other NamesATP1A1;ATPase Na+/K+ transporting subunit alpha 1;ATP1A;CMT2DD;HOMGSMR2
Accession NoUniprot:P05023
GeneID:476
Uniprot
P05023
Gene ID
476
Calculated MW74kDa/109kDa/112kDa/113kDa
Sdspage MW100KDa
FormulationPBS with 0.02% sodium azide,50% glycerol,pH7.3.
StorageStore at -20˚C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
Application Details
WB 1:500 - 1:2000
IHC 1:50 - 1:200
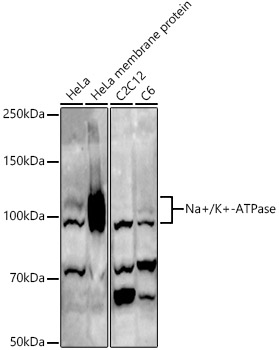
Western blot analysis of extracts of various cell lines, using Na+/K+-ATPase antibody.
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human lung cancer using Na+/K+-ATPase Rabbit pAb.
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded mouse kidney using Na+/K+-ATPase Rabbit pAb.
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human liver cancer using Na+/K+-ATPase Rabbit pAb.
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the family of P-type cation transport ATPases, and to the subfamily of Na+/K+ -ATPases. Na+/K+ -ATPase is an integral membrane protein responsible for establishing and maintaining the electrochemical gradients of Na and K ions across the plasma membrane. These gradients are essential for osmoregulation, for sodium-coupled transport of a variety of organic and inorganic molecules, and for electrical excitability of nerve and muscle. This enzyme is composed of two subunits, a large catalytic subunit (alpha) and a smaller glycoprotein subunit (beta). The catalytic subunit of Na+/K+ -ATPase is encoded by multiple genes. This gene encodes an alpha 1 subunit. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.
If you have published an article using product 55357, please notify us so that we can cite your literature.
et al,Macrophage membrane-mediated targeted curcumin biomimetic nanoparticles delivery for diagnosis and treatment of spinal cord injury by suppressing neuroinflammation and ferroptosis
, (2024),
PMID:





 Yes
Yes



