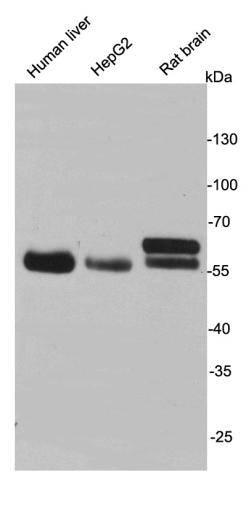
Monoamine oxidase A is an enzyme that degrades amine neurotransmitters, such as dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin. The protein localizes to the outer mitochondrial membrane. Its encoding gene is adjacent to a related gene (MAOB) on the opposite strand of the X chromosome. MAO-A levels in the brain as measured using positron emission tomography are elevated by an average of 34% in patients with major depressive disorder. Genetic association studies examining the relationship between high-activity MAOA variants and depression have produced mixed results, with some studies linking the high-activity variants to major depression in females, depressed suicide in males, major depression and sleep disturbance in males and major depressive disorder in both males and females.