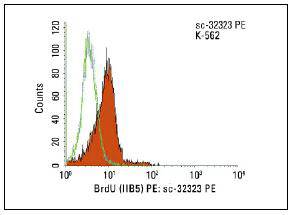
The halogenated pyrimidine thymidine analog bromodeo-xyuridine (BrdU) is incorporated into newly synthesized DNA strands of S-phase cells and is useful for estimating the fraction of cells in S-phase. Additionally, the analysis of the uptake of BrdU is a reliable method to quantitate the degree of DNA-synthesis. BrdU is also useful for studying sister chromatid exchange and to isolate nascent DNA. UV-induced excision-repair synthesis is one method for incorporating BrdU into cellular DNA. Anti-BrdU antibodies bind to the exposed BrdU in single-stranded DNA after a hydrochloric acid denaturation step or nuclease digestion. Protease antigen recovery is necessary for most tissues or cells fixed with crosslinking agents such as formalin but may decrease the specificity of BrdUrd immunodetection. The monoclonal antibody Bu20a against BrdU stains BrdU incorporated into the nulcei of a wide range of proliferating cell types including human tumors growing in nude mice and tonsil lymphoid.