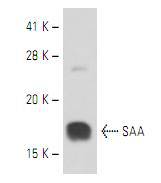
The serum Amyloid A (SAA) family of proteins is encoded by muliple genes, which display allelic variation and a high degree of homology in mammals. The four members of the SAA gene family are clustered on human chromo- some 11p15.1. Three SAA genes are differentially expressed and encode small apolipoproteins. SAA1 and SAA2 encode the acute phase SAAs (A-SAAs) and SAA4 encodes the constitutively expressed SAA (C-SAA). A fourth locus, SAA3, is a pseudogene that contains two C/EBP-binding sites and a third site, which interacts with SAA3 enhancer factor . Human SAA proteins are a group of apolipoproteins found predominantly in the high-density lipoprotein (HDL) fraction of plasma. SAA is a major acute-phase protein and precursor to Amyloid A protein, which is the major constituent of the fibril deposits of reactive amyloidosis. SAA is secreted in large amounts by the liver during microbial infections or inflammatory diseases.