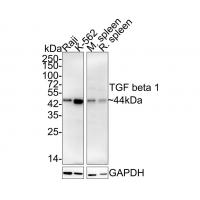
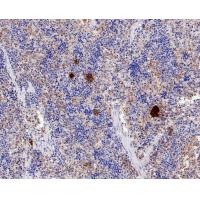
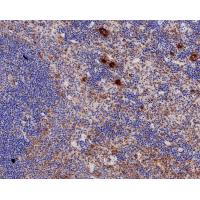
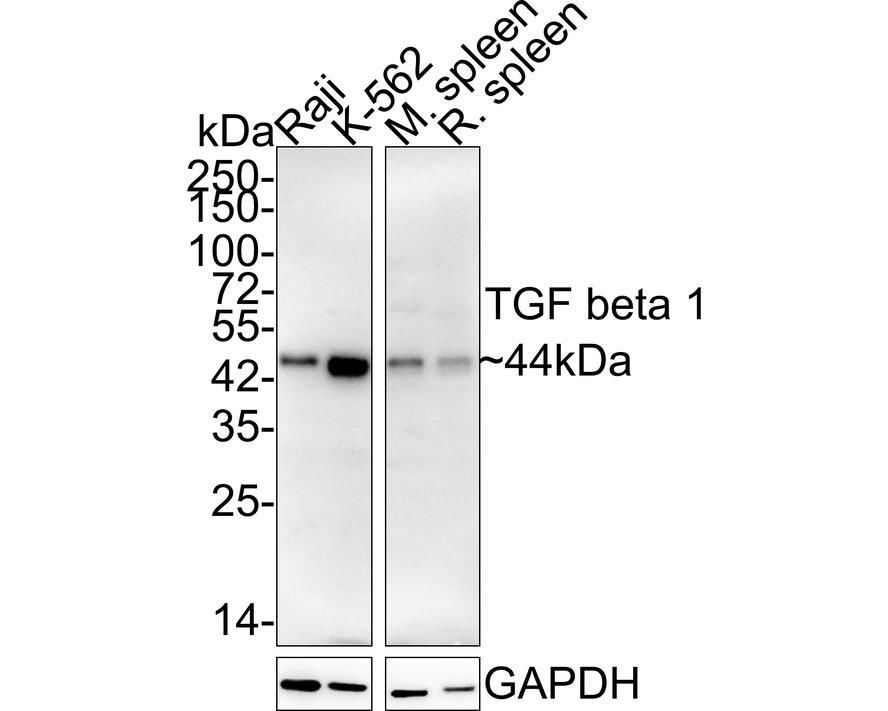
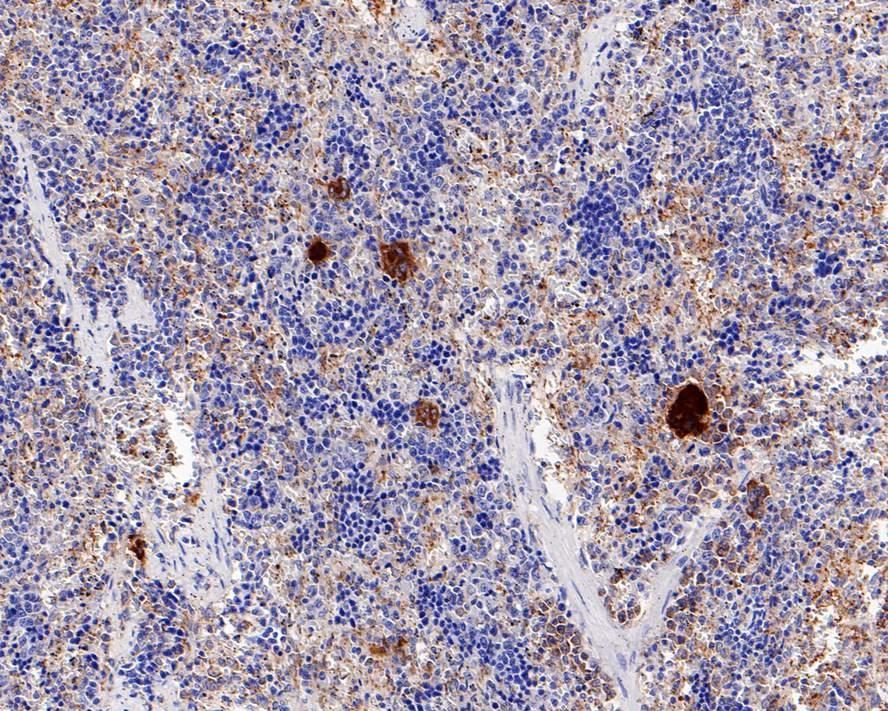
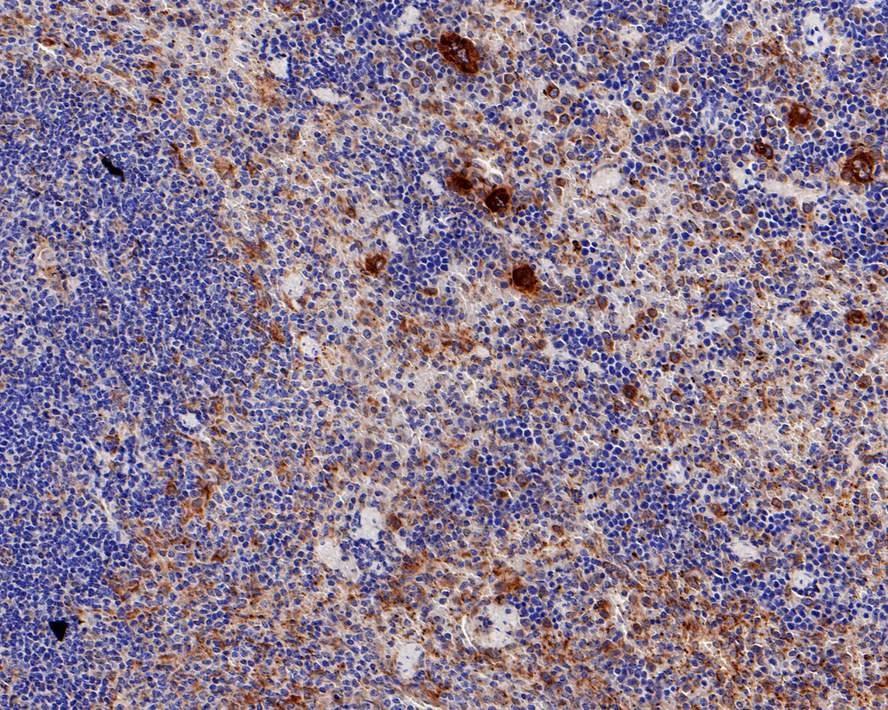
Many cells synthesize TGFB1 and have specific receptors for it. It positively and negatively regulates many other growth factors. It plays an important role in bone remodeling as it is a potent stimulator of osteoblastic bone formation, causing chemotaxis, proliferation and differentiation in committed osteoblasts. Heterodimers of TGFB1/TGFB2 have been found in bone. Interacts with CD109 and DPT. Interacts with ASPN. Function: TGF beta 2 has suppressive effects on interleukin-2 dependent T-cell growth. Tissue specificity: TGF beta 1 is highly expressed in bone. A chromosomal aberration involving TGFB2 is found in a family with Peters anomaly.