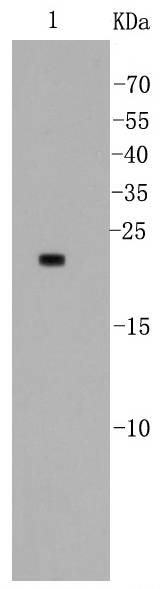
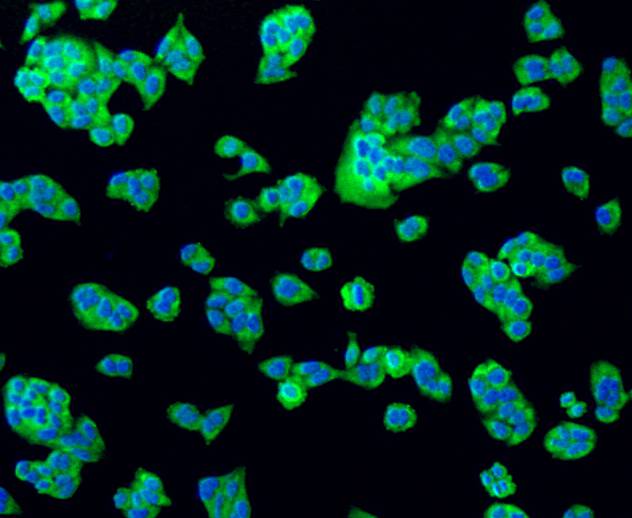
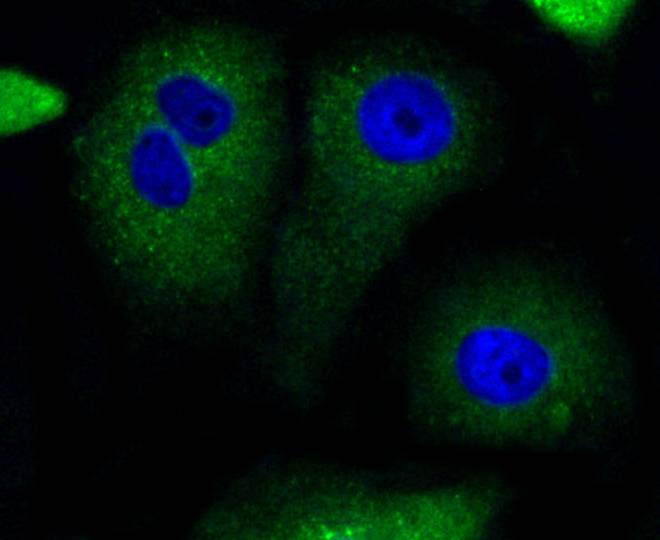
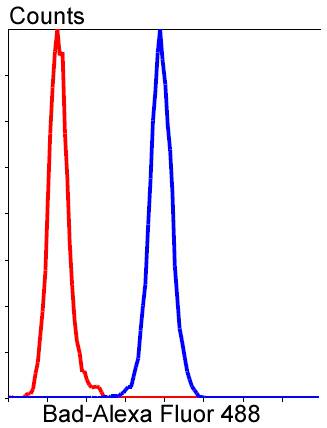
The Bcl-2 family of proteins is characterized by its ability to modulate cell death (apoptosis) under a broad range of physiologic conditions. Bcl-2 and several related proteins function to inhibit apoptosis while other members of the Bcl-2 family, such as Bax and Bak, enhance cell death under various conditions. For instance, Bcl-xL represses cell death, while its shorter form, Bcl-xS, promotes apoptosis. A protein designated Bad exhibits homology to Bcl-2 limited to the BH1 and BH2 domains. Bad functions to dimerize with Bcl-xL and with Bcl-2, but not with Bax, Bcl-xS, Mcl-1, A1 or itself. In mammalian cells, Bad binds with greater affinity to Bcl-xL than to Bcl-2 and reverses the death repressor activity of Bcl-xL but not Bcl-2. Dimerization of Bad with Bcl-xL results in displacement of Bax from Bcl-xL:Bax complexes thereby causing restoration of Bax-mediated apoptosis.