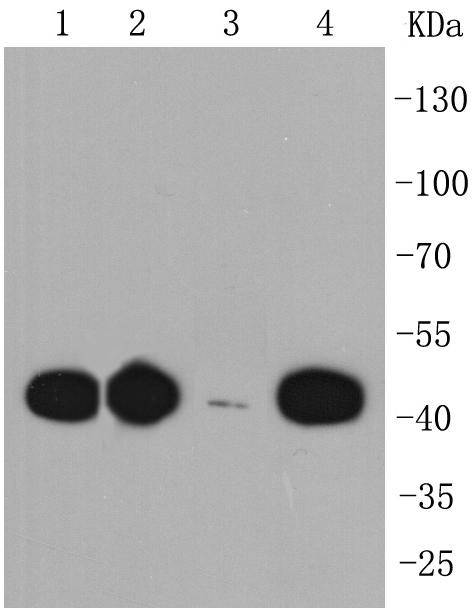
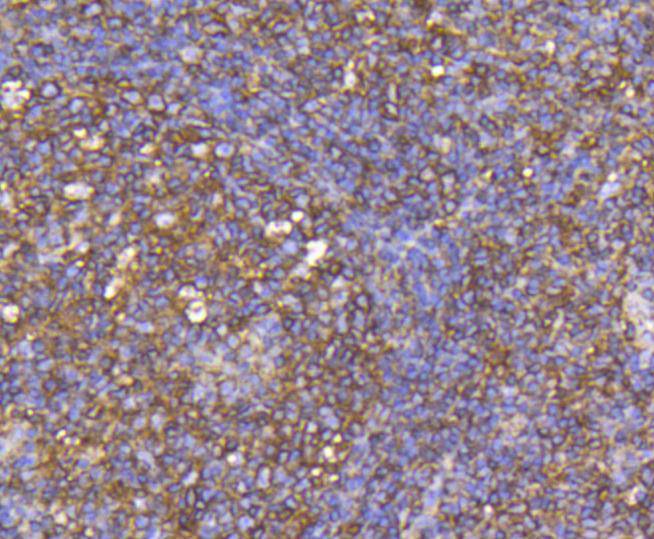
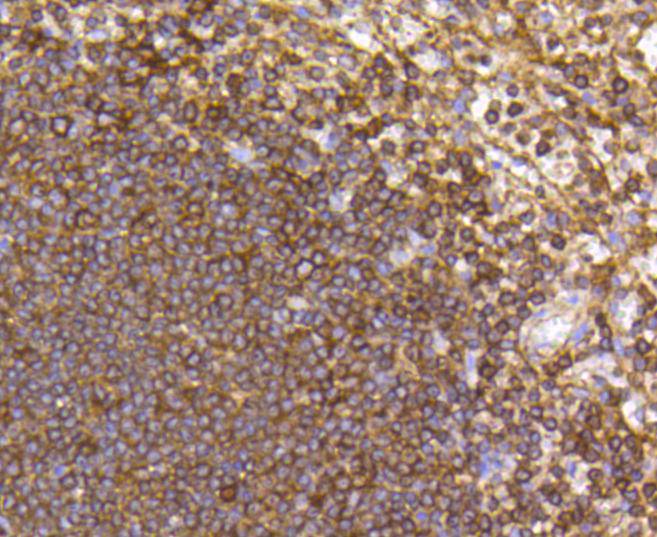
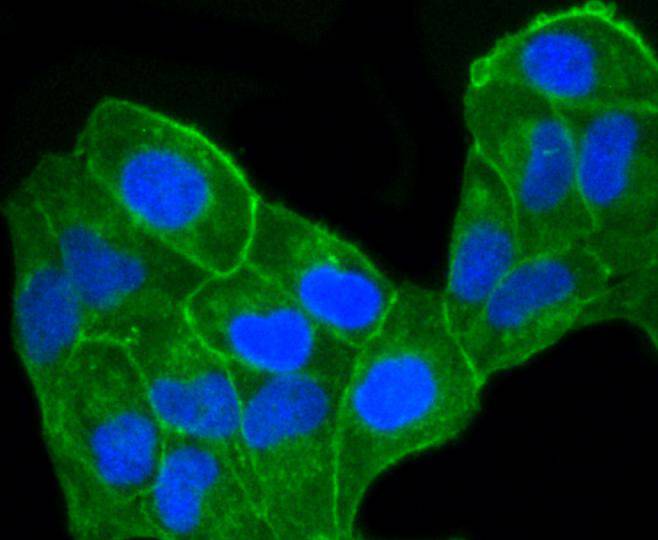
C-C or chemokine family members are characterized by a pair of adjacent cysteine residues and serve as potent chemoattractants and activators of monocytes and T cells. C-C chemokine receptor family members include CKR-1, CKR-2A, CKR-2B, CKR-3, CKR-4, CKR-5, CKR-6, CKR-7, CKR-8, CKR-9, CKR-10 and the Duffy blood group antigen. Each of these receptors are G protein-coupled, seven pass transmembrane domain proteins whose major physiological role is to function in the chemotaxis of T cells and phagocytic cells to areas of inflammation. However, this receptor family has also been shown to facilitate viral infection. CKR-7 (C-C chemokine receptor type 7), also known as CCR7, CMKBR7, EBI1 or EVI1, is a 378 amino acid multi-pass membrane protein that belongs to the CC-chemokine receptor family. Expressed in activated B- and T-lymphocytes, as well as in various lymphoid tissues, CKR-7 functions as a receptor for MIP-3 and is thought to be involved in mediating normal lymphocyte function.