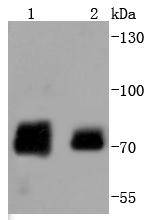
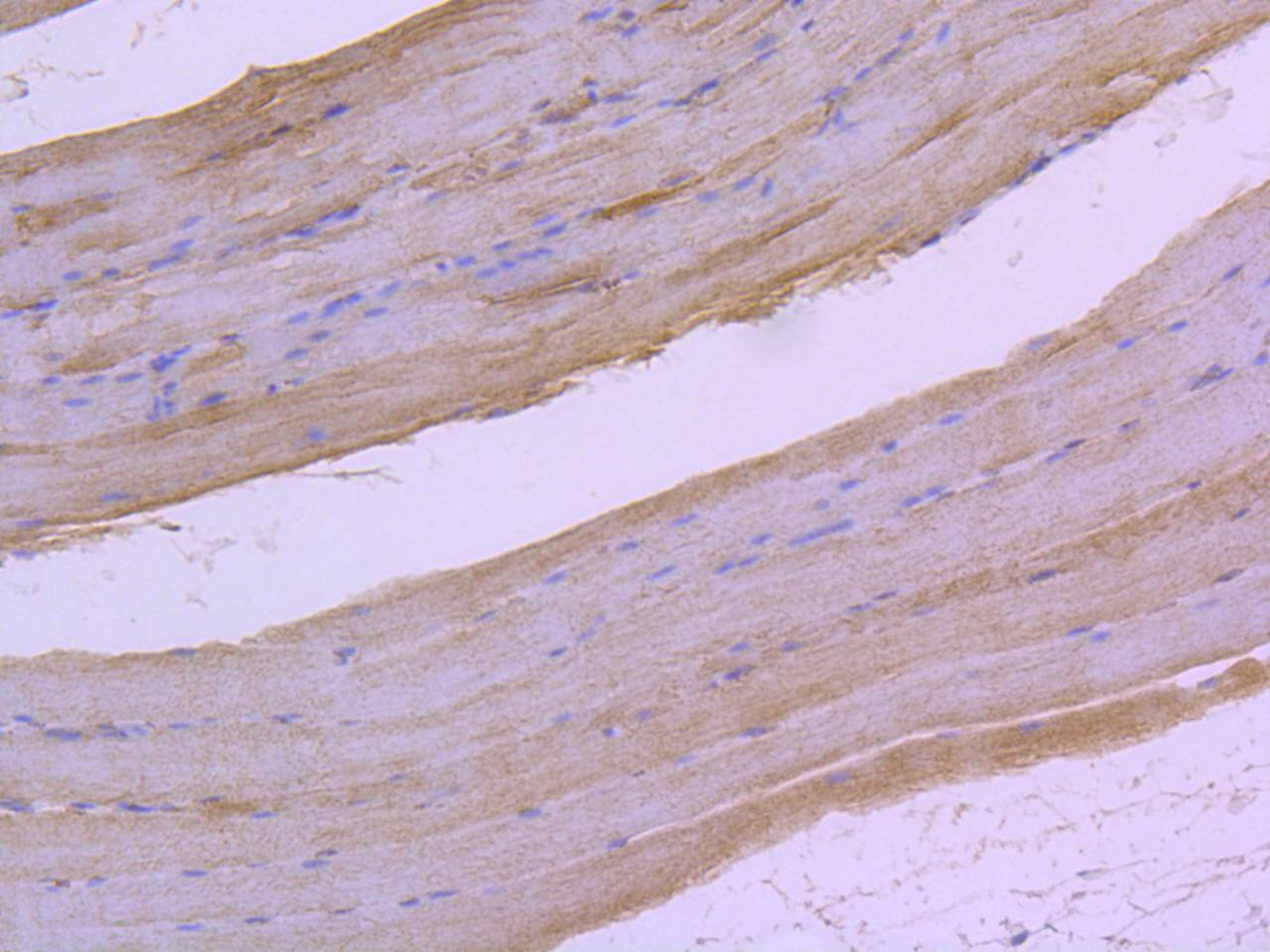
Raf-1 is a ubiquitously expressed cytoplasmic protein with intrinsic serine/threonine kinase activity. Raf-1, or c-Raf, is the cellular homolog of v-Raf, the product of the transforming gene of the 3611 strain of murine sarcoma virus. The unregulated kinase activity of the v-Raf protein is associated with cellular transformation and mitogenesis. Raf-1 is normally suppressed by its regulatory N-terminal domain. Raf-1 is activated in response to a variety of tyrosine kinase receptors as well as in response to pp60v-Src expression. Specifically, Raf-1 is phosphorylated in the catalytic domain at Ser 338 and, to a lesser extent, Ser 339. This phosphorylation requires the co-activation of PI 3-kinase and the Ras signaling pathway. Raf-1 is also phosphorylated on Tyr 340 and 341, which induces the phosphorylation of MEK. Phosphorylation of Ser 621 is essential for the catalytic activity of Raf-1 and downregulation by c-AMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA). PKA also phosphorylates Raf-1 on Ser 43 and Ser 259. PKA phosphorylation of Ser 259 inhibits Raf-1 and decreases the phosphorylation necessary for Raf-1 activation at Ser 338.