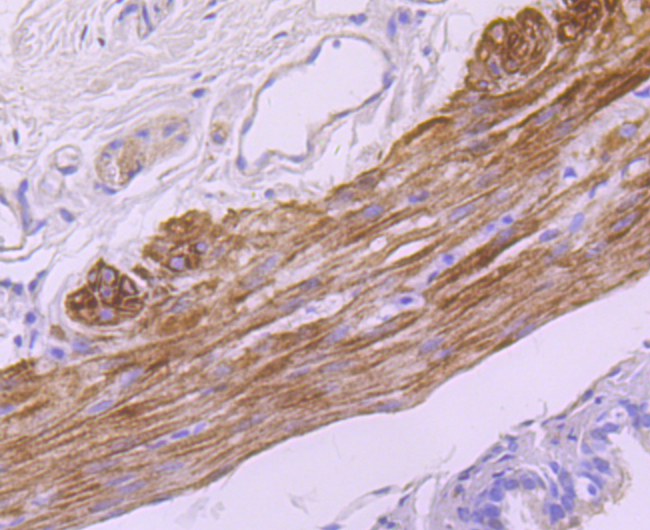
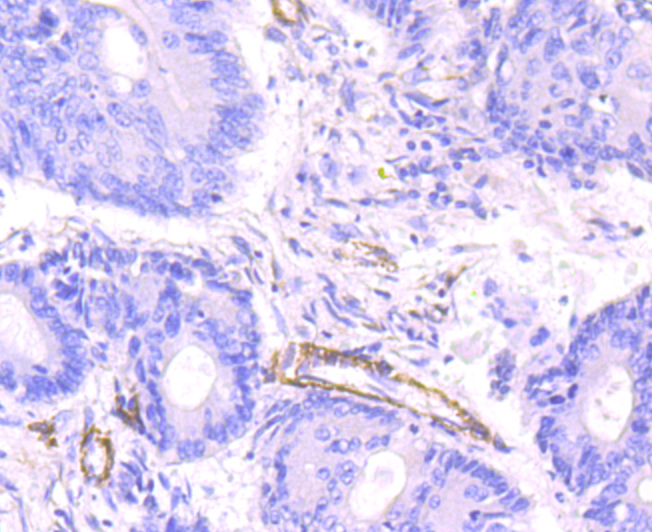
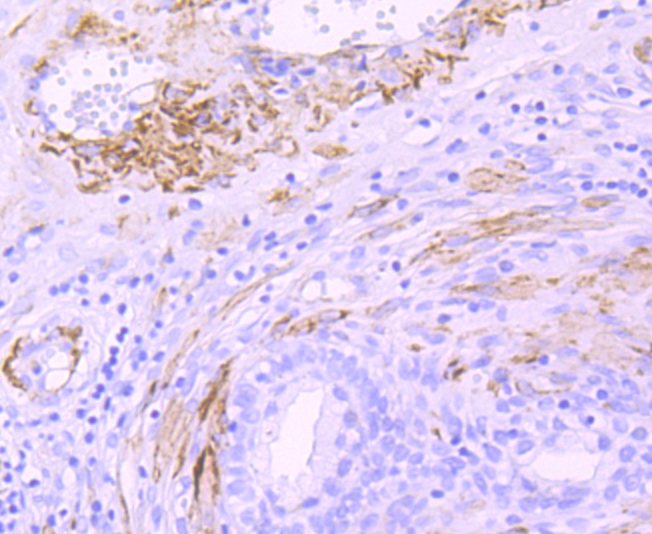
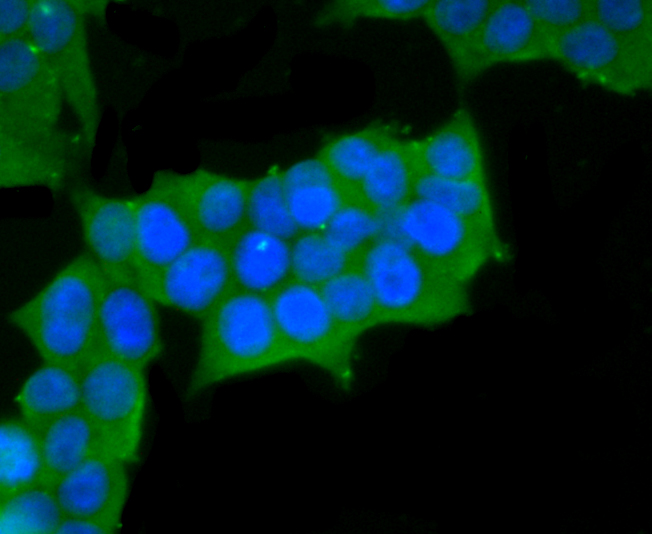
Myosin is a highly conserved, ubiquitously expressed protein that interacts with Actin to generate the force for cellular movements. Conventional Myosins are hexameric proteins consisting of two heavy chain subunits, a pair of non-phosphorylatable light chain subunits and a pair of phosphorylatable light chain subunits, which is expressed by my calcium and calmodulin-dependent phosphorylation of Myosin light chain (MLC) Myosin heavy chains, encoded by the MYH gene family, contain Actin-activated ATPase activity which generates the motor function of Myosin. Myosin heavy chains were initially isolated from a human fetal skeletal muscle and are the major determinant in the Speed of contraction of skeletal muscle. Various isoforms of myosin heavy chains are differentially expressed depending on th E functional activity of the muscle.