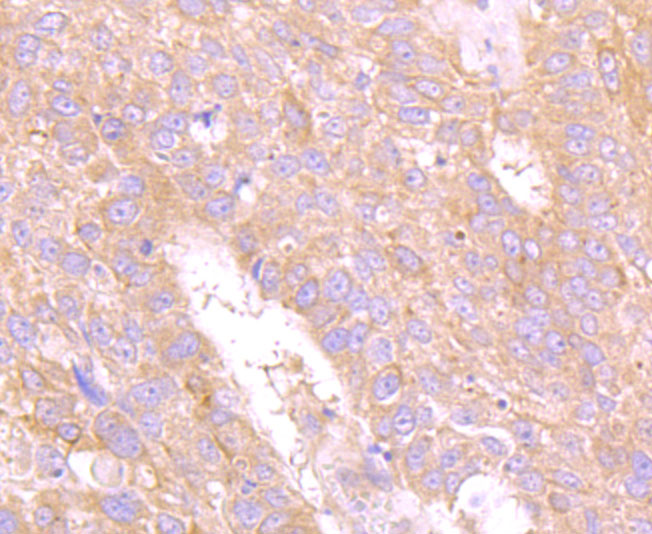
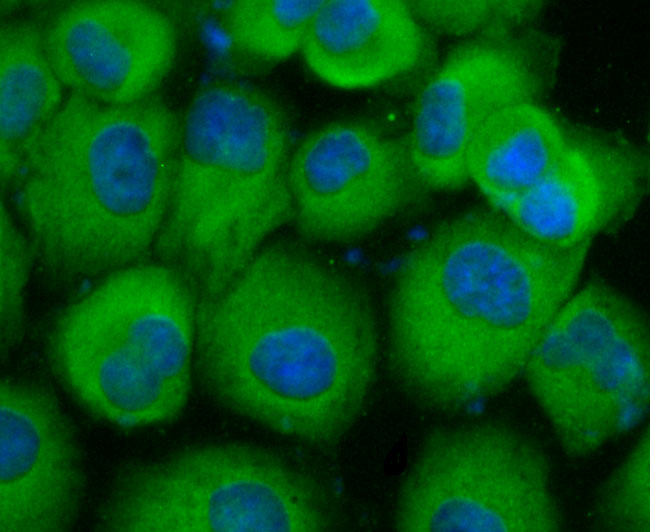
The CD66 (carcinoembryonic antigen, CEA, biliary glycoprotein I, BGP-1, CEACAM) immunoglobulin superfamily of genes encode cell adhesion proteins, which are expressed at higher levels in tumorous tissues than in normal tissues. The human CD66 gene family is a diverse set of glycoproteins of epithelial and hematopoietic lineage that comprises 29 genes, which map to chromosome position 19q13.1-q13.2. CD66A, CD66B, CD66C, CD66D, CD66E and CD66F are the best characterized CD66 antigens, and CD66A-D expression upregulates on the surface of granulocytes upon stimulation. Certain CD66 family members mediate homotypic and heterotypic intercellular adhesion events. CD66E, also known as CEA, is a well known tumor marker and a heavily glycosylated GPI-linked cell surface molecule.