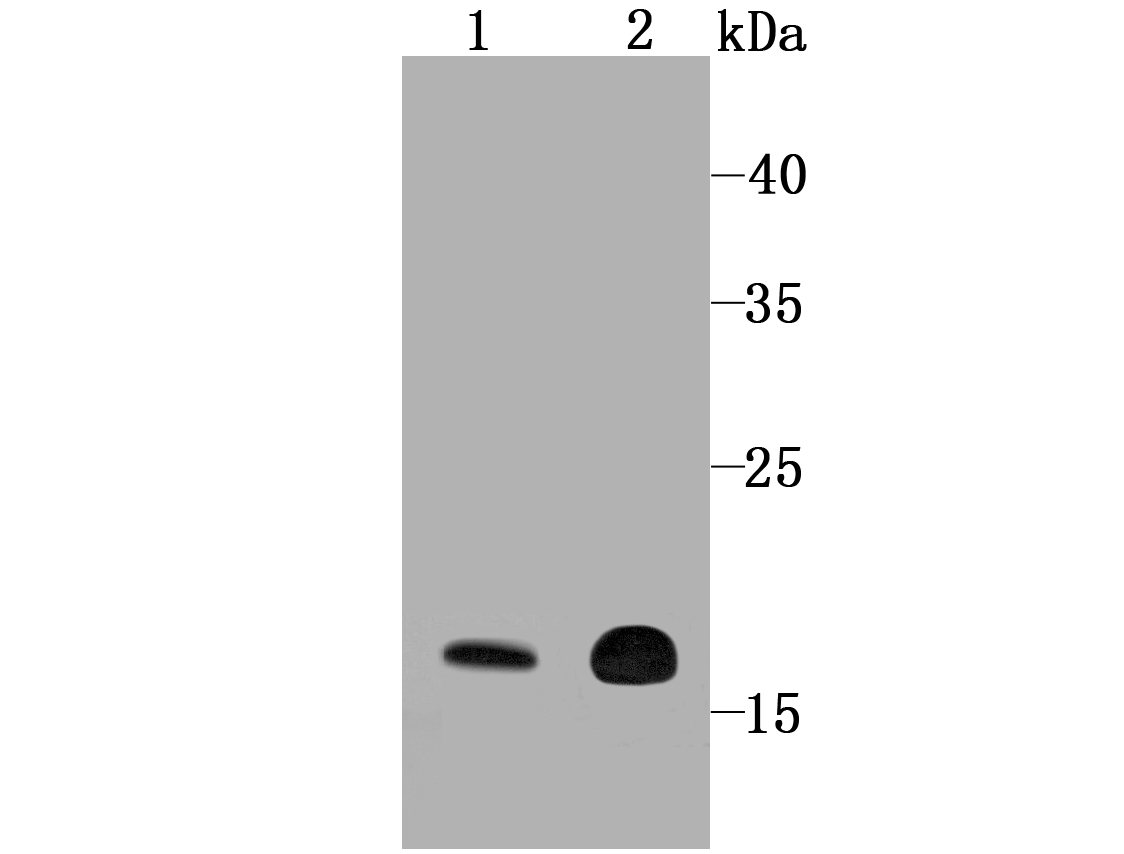
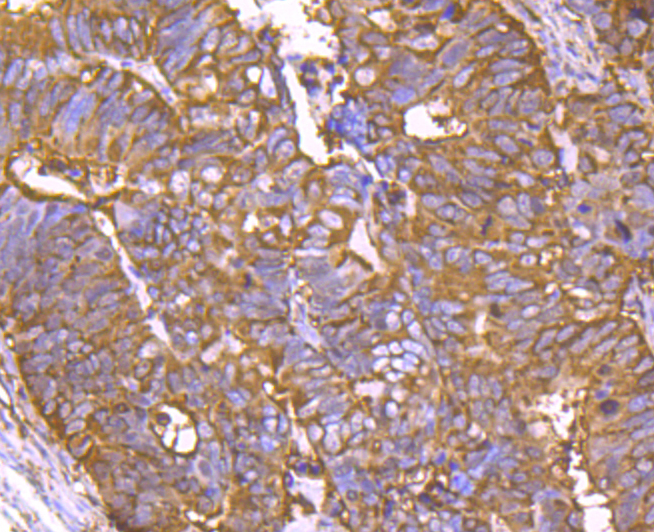
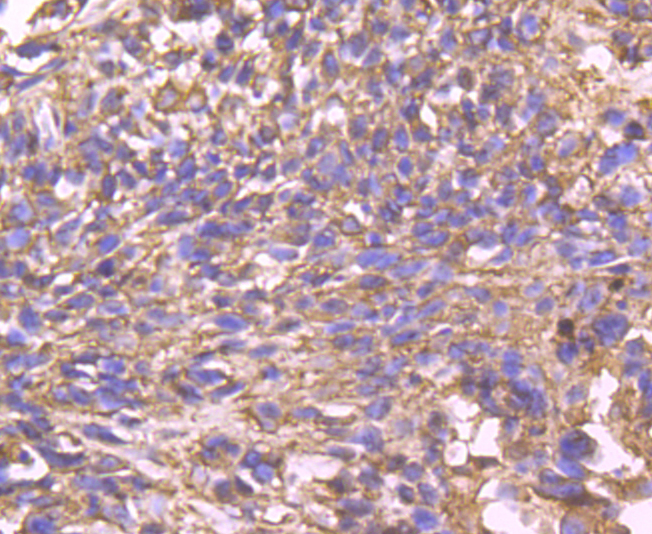
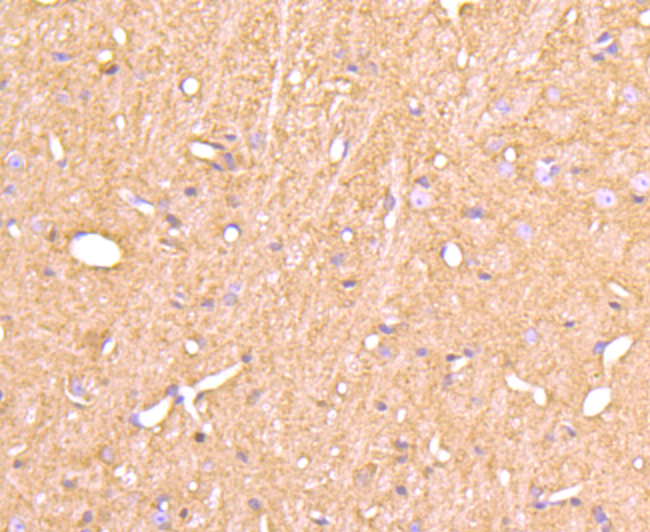
Cyclophilins are conserved, ubiquitous and abundant cytosolic peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerases that accelerate the isomerization of XaaPro peptide bonds and the refolding of proteins. Human cyclophilin A (CyPA), an intracellular protein of 165 amino acids, is the target of cyclosporin A (CsA) and is encoded by a single unique gene conserved between yeast to humans. Cyclophilin B (CyPB) is secreted in biological fluids such as blood or milk, and binds to a specific receptor present on human peripheral blood lymphocytes and expressed in Jurkat cells, a line of human lymphoblasts. Cyclophilin D (CyP40) is a widely expressed cytoplasmic protein that catalyzes the cis-trans isomerization of proline imidic peptide bonds in oligopeptides. Cyclophilin F (CyP3), is also known as PPIF, Cyp-D or Rotamase F, is a 207 amino acid mitochondrial matrix protein involved in the induction of necrotic and apoptotic cell death through the activation of the mitochondrial permeability transition (mPT) pore.