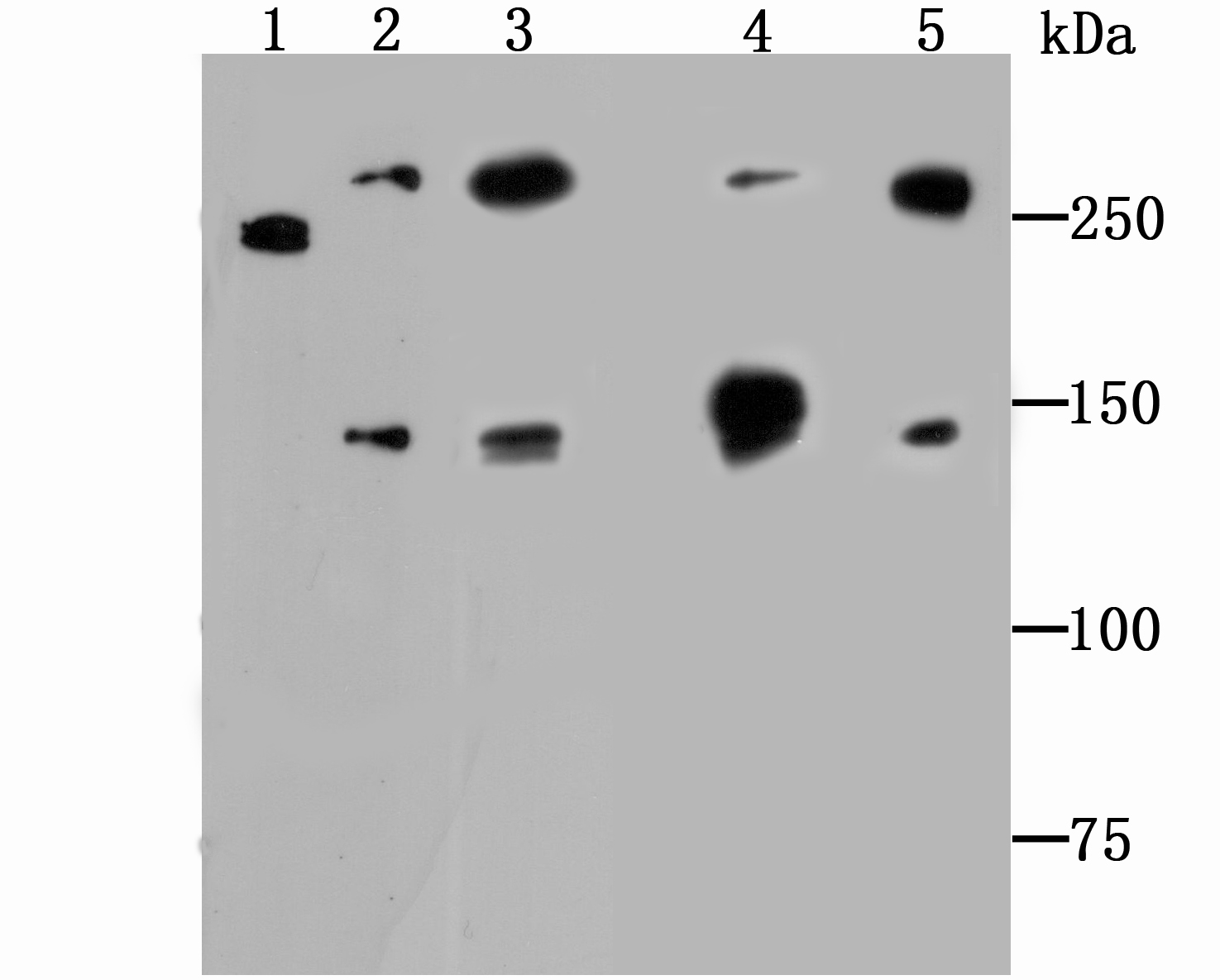
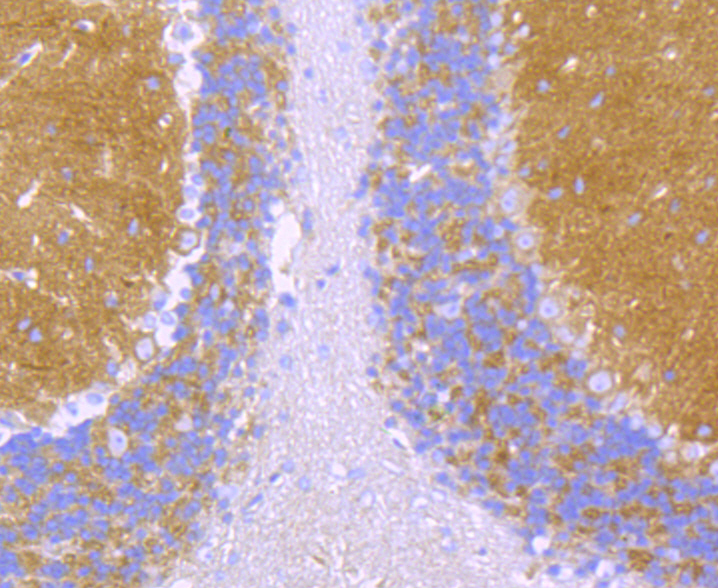
Alpha Fodrin also named Spectrin. Spectrin, an actin binding protein that is a major component of the cytoskeletal superstructure of the erythrocyte plasma membrane, is essential in determining the properties of the membrane including its shape and deformability. Spectrins function as membrane organizers and stabilizers, composed of nonhomologous α and β chains, which aggregate side-to-side in an antiparallel fashion to form dimers, tetramers, and higher polymers. Spectrin α I and spectrin β I are present in erythrocytes, whereas spectrin α II (also designated fodrin α) and spectrin β II (also designated fodrin β) are present in other somatic cells. The spectrin tetramers in erythrocytes act as barriers to lateral diffusion, but spectrin dimers seem to lack this function. Activation of calpain results in the breakdown of spectrin α II, a neuronal cytoskeleton protein.