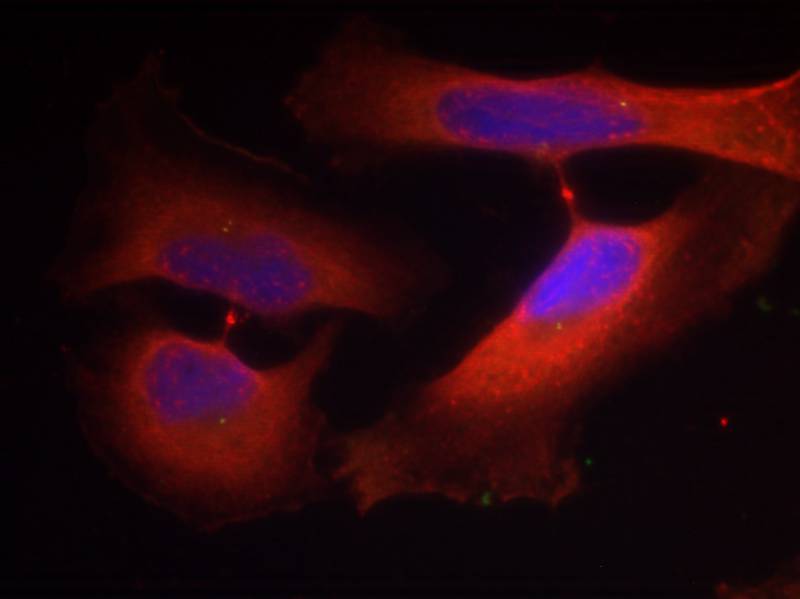
Keratin 8 is a member of the type II keratin family clustered on the long arm of chromosome 12. Type I and type II keratins heteropolymerize to form intermediate-sized filaments in the cytoplasm of epithelial cells. The product of this gene typically dimerizes with keratin 18 to form an intermediate filament in simple single-layered epithelial cells. This protein plays a role in maintaining cellular structural integrity and also functions in signal transduction and cellular differentiation. Mutations in this gene cause cryptogenic cirrhosis.
Nakamichi I, et al. (2002) Mol Biol Cell; 13(10): 3441-3451.
Prochasson P, et al. (2002) Nucleic Acids Res; 30(15): 3312-3322.
Pankov R, et al. (1994) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A; 91(3): 873-877.
Thorey IS, et al. (1993) Mol Cell Biol; 13(11): 6742-6751