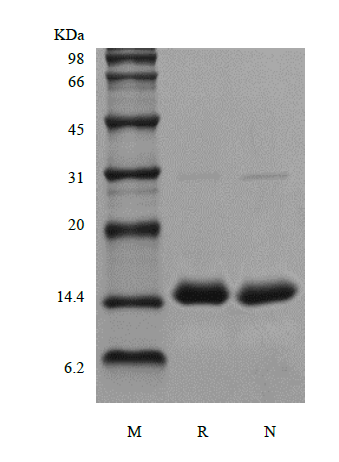
Procalcitonin (PCT) belongs to a group of related proteins including calcitonin gene-related peptides I and II, amylin, adrenomodulin and calcitonin (CAPA peptide family). PCT, like other peptides of CAPA family, appears from the common precursor pre-procalcitonin consisting of 141 amino acids by removal of 25 amino acids from the N-terminus. PCT undergoes successive cleavages to form three molecules: N-terminal fragment (55 a.a.), calcitonin (32 a.a.) and katacalcin (21 a.a.). PCT is a peptide precursor of the hormone calcitonin, the latter being involved with calcium homeostasis. PCT is produced by parafollicular cells (C cells) of the thyroid and by the neuroendocrine cells of the lung and the intestine. But its level is related to the severity of bacterial sepsis, it is considered to be one of the earliest and most specific markers of sepsis.