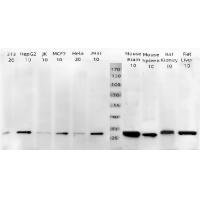
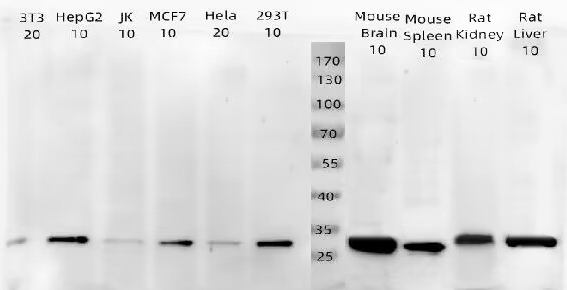
BCL2 exerts a survival function in response to a wide range of apoptotic stimuli through inhibition of mitochondrial cytochrome c release (1). It has been implicated in modulating mitochondrial calcium homeostasis and proton flux (2). Several phosphorylation sites have been identified within BCL2 including Thr56, Ser70, Thr74 and Ser87 (3). It has been suggested that these phosphorylation sites may be targets of the ASK1/MKK7/JNK1 pathway, and that phosphorylation of BCL2 may be a marker for mitotic events (4,5). Mutation of BCL2 at Thr56 or Ser87 inhibits its anti-apoptotic activity during glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis of T lymphocytes (6). Interleukin 3 and JNK-induced BCL2 phosphorylation at Ser70 may be required for its enhanced anti-apoptotic functions (7).