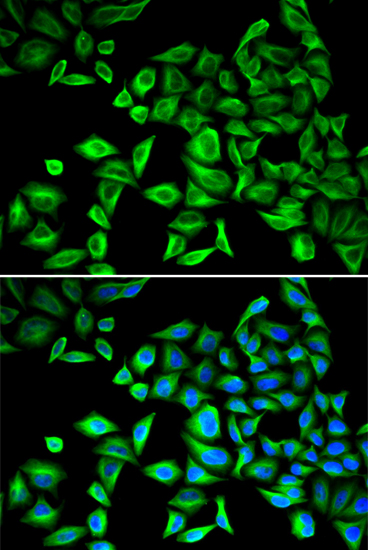
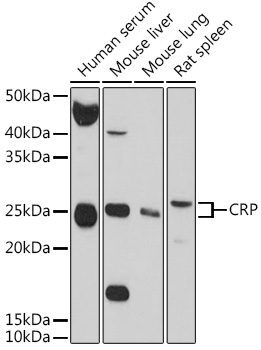
Human c-Reactive protein (CRP) was discovered in serum of patients as a nonantibody precipitin of the C-polysaccharide from pneumococci(1). During acute infection, the amounts of circulating CPR increases 100-1000 fold (2). Serum CRP values are routinely measured to detect or monitor many human diseases and minor elevations of C-reactive protein are predictive of cardiovascular events in patients with coronary heart disease (3). CRP promotes host defense, is an efficient activator of the classical C cascade, and shown to be opsonic (4).The opsonic and C activation activities are responsible for the nonspecific host defense activities providing protection in the preimmune stage of acute infections. Additionally, IL-1 and IL-6 are known to stimulate CRP biosynthesis (5).